Enhancing Military Displays: Options for Improved Performance and Durability
11 December, 2025
Enhancing Military Displays: Options for Improved Performance and Durability
In military applications, display systems are critical for situational awareness, command and control, and mission success. These displays must operate reliably in harsh environments, withstand physical stress, and provide clear, usable interfaces under diverse conditions. To meet these demands, several advanced options can be integrated into display systems, including resistive multi-touch panels, cover glass with anti-UV coatings, optical bonding, and shatter- and impact-resistant glass. This article explores these technologies and their benefits for military applications.
Resistive Multi-Touch Panels
Resistive multi-touch panels are widely used in military displays due to their versatility and reliability in rugged environments. These panels operate by detecting pressure applied to the screen, which causes two conductive layers to make contact and register input. Unlike capacitive touchscreens, resistive panels can be operated with gloves, styluses, or other tools, making them ideal for military personnel who often work in extreme conditions or wear protective gear.
Benefits for Military Applications:
- Durability: Resistive panels are robust and can function in environments with dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures, which are common in military operations.
- Versatility: They support input from various sources, including gloved hands or improvised tools, ensuring usability in field conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Resistive panels are generally less expensive than other touch technologies, allowing for cost-efficient integration into military systems.
- Multi-Touch Capability: Modern resistive panels support multi-touch gestures, enabling intuitive interfaces for tasks like zooming in on maps or controlling complex systems.
Considerations: Resistive panels may have slightly lower optical clarity compared to capacitive screens and can be less responsive to light touches. However, their ruggedness and flexibility make them a staple for military applications where reliability is paramount.
2. Cover Glass with Anti-UV Coatings
Military displays are often exposed to intense sunlight, which can degrade visibility and damage internal components over time. Cover glass with anti-ultraviolet (UV) coatings addresses these challenges by protecting the display and enhancing performance in bright environments.
Benefits for Military Applications:
- Improved Visibility: Anti-UV coatings reduce glare and reflections, ensuring clear visibility in direct sunlight, which is critical for outdoor operations.
- Component Protection: UV coatings block harmful ultraviolet rays that can degrade display materials, extending the lifespan of the screen.
- Enhanced Durability: These coatings can be combined with other protective layers, such as anti-scratch or anti-fingerprint treatments, to maintain display integrity in rugged conditions.
Considerations: The application of anti-UV coatings must be carefully engineered to avoid compromising touch sensitivity or adding excessive weight to portable devices. High-quality coatings are essential to ensure long-term performance without peeling or degradation.
Optical Bonding
Optical bonding is a process that eliminates the air gap between the display panel and the cover glass by using a transparent adhesive. This technique significantly enhances display performance, making it a valuable addition for military applications.
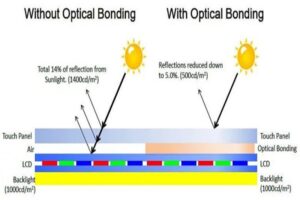
Benefits for Military Applications:
- Enhanced Readability: By reducing internal reflections, optical bonding improves contrast and visibility, even in bright sunlight or low-light conditions.
- Increased Durability: The adhesive layer adds structural integrity, making the display more resistant to shocks, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations.
- Moisture and Dust Resistance: Optical bonding seals the display, preventing ingress of moisture, dust, or other contaminants that could impair performance in harsh environments.
- Reduced Parallax: For touch displays, optical bonding minimises parallax errors, ensuring precise touch input for critical operations.
Considerations: Optical bonding increases manufacturing complexity and cost. Additionally, repairs can be more challenging, as the bonded layers are difficult to separate without damaging the display. However, the performance benefits often outweigh these drawbacks for military use.
Shatter- and Impact-Resistant Glass
Military displays are frequently subjected to physical stress, including impacts, drops, and vibrations. Shatter- and impact-resistant glass, such as chemically strengthened glass (e.g., Gorilla Glass) or laminated glass, is designed to withstand these challenges while maintaining functionality.
Benefits for Military Applications:
- Enhanced Durability: Impact-resistant glass can withstand drops, shocks, and ballistic impacts, ensuring displays remain operational in combat or field conditions.
- Safety: Shatter-resistant glass prevents the display from breaking into sharp fragments, reducing the risk of injury to personnel.
- Lightweight Design: Modern materials like chemically strengthened glass provide high strength without adding significant weight, which is crucial for portable military equipment.
- Compatibility with Other Technologies: Impact-resistant glass can be combined with anti-UV coatings or optical bonding to create a comprehensive solution for rugged displays.
Considerations: While highly durable, shatter-resistant glass can still crack under extreme force, and its cost may be higher than standard glass. Selecting the appropriate thickness and material is critical to balance durability with weight and cost constraints.
Integration and Synergy
The true power of these technologies lies in their integration. For example, a military display could feature a resistive multi-touch panel for glove-compatible operation, optical bonding for enhanced readability and durability, anti-UV coated cover glass for sunlight visibility, and shatter-resistant glass for impact protection. This combination creates a display that is robust, user-friendly, and capable of performing in the most demanding environments.
Practical Applications in Military Contexts:
- Vehicle-Mounted Displays: Displays in tanks, aircraft, or naval vessels benefit from optical bonding and impact-resistant glass to withstand vibrations and potential impacts.
- Portable Devices: Handheld devices used by soldiers, such as rugged tablets or GPS units, rely on resistive multi-touch panels and shatter-resistant glass for field usability.
- Command Centres: Large displays in command centres can leverage anti-UV coatings and optical bonding to ensure clear visibility under varying lighting conditions.
Challenges and Future Directions
While these technologies significantly enhance military displays, challenges remain. Cost is a major consideration, as integrating multiple enhancements can increase production expenses. Additionally, ensuring compatibility between technologies (e.g., maintaining touch sensitivity with thick protective glass) requires careful engineering.
Looking ahead, advancements in materials science, such as flexible displays or self-healing glass, could further revolutionise military displays. Additionally, integrating augmented reality (AR) or heads-up display (HUD) technologies with these enhancements could provide soldiers with real-time, mission-critical information in a highly durable format.
Conclusion
Resistive multi-touch panels, anti-UV coated cover glass, optical bonding, and shatter- and impact-resistant glass are essential technologies for enhancing military displays. Each offers unique benefits, from improved usability and readability to increased durability and safety. By combining these options, military systems can achieve the reliability and performance needed to operate in extreme conditions, ensuring mission success and personnel safety. As technology evolves, continued innovation in display enhancements will further strengthen their role in military applications.